【FFmpeg】FFmpeg 函数简介 ③ ( 编解码相关函数 | FFmpeg 源码地址 | FFmpeg 解码器相关 结构体 和 函数 )
文章目录
- 一、FFmpeg 解码器简介
- 1、解码流程分析
- 2、FFmpeg 编解码器 本质
- 3、FFmpeg 编解码器 ID 和 名称
- 二、FFmpeg 解码器相关 结构体 / 函数
- 1、AVFormatContext 结构体
- 2、avcodec_find_decoder 函数 - 根据 ID 查找 解码器
- 3、avcodec_find_decoder_by_name 函数 - 根据 名称 查找 解码器
- 4、avcodec_alloc_context3 函数 - 初始化编解码上下文结构体
- 5、avcodec_parameters_to_context 函数 - 拷贝 编解码上下文结构体 数据
- 6、avcodec_open2 函数 - 打开编解码器
- 7、avcodec_send_packet 函数 和 avcodec_receive_frame 函数 - 解码组合函数
- 8、avcodec_free_context 函数 和 avcodec_close 函数 - 释放编解码器上下文结构体
FFmpeg 4.0 版本源码地址 :
- GitHub : https://github.com/FFmpeg/FFmpeg/tree/release/4.0
- GitCode : https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/ff/FFmpeg/tree/release/4.0
一、FFmpeg 解码器简介
1、解码流程分析
音视频 解码 相关函数 , 对应下图 红色矩形框区域 中的操作 :
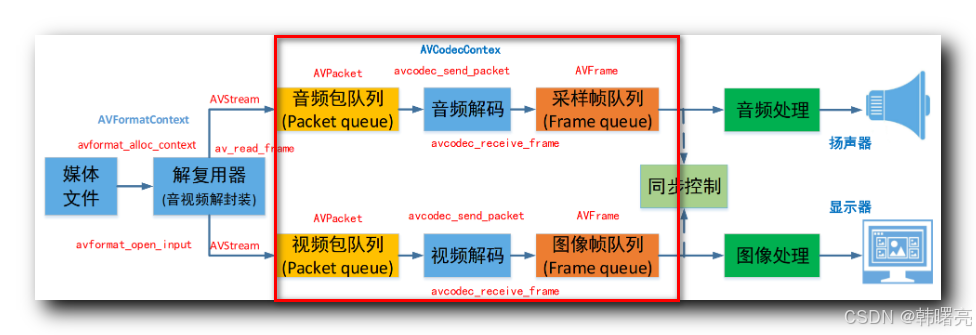
音视频 解码流程 如下图所示 :
- 首先 , 调用 avcodec_alloc_context3 函数 , 分配解码器上下文 AVCodecContext 结构体对象 ;
- 然后 , 调用 avcodec_parameters_to_context 函数 , 将 编解码器 信息拷贝到 AVCodecContext 结构体对象 中 ;
- 再后 , 调用 avcodec_find_decoder 函数 或者 avcodec_find_decoder_by_name 函数 , 查找相应的编解码器 ;
- 之后 , 调用 avcodec_open2 函数 , 打开编解码器 , 并与 AVCodecContext 结构体对象 进行关联 ;
- 最后 , 进行 逐包 循环解码 , 先调用 avcodec_send_packet 函数 , 向解码器发送数据包 , 然后调用 avcodec_receive_frame 函数 , 从解码器获取解码后的数据帧 ;
程序执行完毕后 , 调用 avcodec_free_context 函数 或者 avcodec_close 函数 , 释放编解码器占用的资源 , 上述函数中 avcodec_free_context 函数 包含 avcodec_close 函数 ;

2、FFmpeg 编解码器 本质
H.264 只是一个 编解码器 规范标准 , 不同的 厂家 会根据该 规范 开发 不同的编解码器 ,
下面的代码是 FFmpeg 中定义的 H.264 规范的 解码器 , 这是一个 AVCodec 类型的结构体对象 , 该结构体对象中 包含了与 H.264 编解码器 相关的所有必要数据和函数指针 , 用于初始化、解码、关闭等操作 ;
AVCodec ff_h264_decoder = {.name = "h264", // 编解码器名称.long_name = NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL("H.264 / AVC / MPEG-4 AVC / MPEG-4 part 10"), // 编解码器的全名.type = AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO, // 媒体类型(视频).id = AV_CODEC_ID_H264, // 编解码器ID.priv_data_size = sizeof(H264Context), // 私有数据大小,H264上下文结构的大小.init = h264_decode_init, // 初始化函数.close = h264_decode_end, // 关闭函数.decode = h264_decode_frame, // 解码函数.capabilities = /*AV_CODEC_CAP_DRAW_HORIZ_BAND |*/ AV_CODEC_CAP_DR1 | // 编解码器能力AV_CODEC_CAP_DELAY | AV_CODEC_CAP_SLICE_THREADS | AV_CODEC_CAP_FRAME_THREADS,.hw_configs = (const AVCodecHWConfigInternal*[]) { // 硬件加速配置
#if CONFIG_H264_DXVA2_HWACCELHWACCEL_DXVA2(h264), // DXVA2 硬件加速
#endif
#if CONFIG_H264_D3D11VA_HWACCELHWACCEL_D3D11VA(h264), // D3D11VA 硬件加速
#endif
#if CONFIG_H264_D3D11VA2_HWACCELHWACCEL_D3D11VA2(h264), // D3D11VA2 硬件加速
#endif
#if CONFIG_H264_NVDEC_HWACCELHWACCEL_NVDEC(h264), // NVDEC 硬件加速
#endif
#if CONFIG_H264_VAAPI_HWACCELHWACCEL_VAAPI(h264), // VAAPI 硬件加速
#endif
#if CONFIG_H264_VDPAU_HWACCELHWACCEL_VDPAU(h264), // VDPAU 硬件加速
#endif
#if CONFIG_H264_VIDEOTOOLBOX_HWACCELHWACCEL_VIDEOTOOLBOX(h264), // VideoToolbox 硬件加速
#endifNULL // 结束标记},.caps_internal = FF_CODEC_CAP_INIT_THREADSAFE | FF_CODEC_CAP_EXPORTS_CROPPING, // 内部能力标志.flush = flush_dpb, // 刷新函数.init_thread_copy = ONLY_IF_THREADS_ENABLED(decode_init_thread_copy), // 线程复制初始化.update_thread_context = ONLY_IF_THREADS_ENABLED(ff_h264_update_thread_context), // 更新线程上下文.profiles = NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL(ff_h264_profiles), // 配置文件.priv_class = &h264_class, // 私有类
};
源码地址 : https://github.com/FFmpeg/FFmpeg/blob/release/4.0/libavcodec/h264dec.c Line1047 ~ 1089
FFmpeg 4.0 版本源码地址 : https://github.com/FFmpeg/FFmpeg/tree/release/4.0
3、FFmpeg 编解码器 ID 和 名称
下面分析 编解码器的 名称 和 编码器 ID 字段 ;
avcodec_find_decoder 函数 是 根据 编解码器ID 查找 FFmpeg 中的编解码器的 ;
avcodec_find_decoder_by_name 函数 是根据 编解码器名称 查找 FFmpeg 中的编解码器的 ;
.name = "h264", // 编解码器名称 就是为该编解码器定义的名称 , 可以直接在 FFmpeg 命令中通过该 名称 " h264 " 调用该 编解码器 ;
.id = AV_CODEC_ID_H264, // 编解码器ID 是 编解码器的 ID , 这是一个 枚举 , 定义在 libavcodec/avcodec.h 代码中 , AV_CODEC_ID_H264 是 FFmpeg 对 H.264 编码的 内部表示 , 只要是 H.264 规范的编解码器 , 不管是哪家厂商开发 H.264 的编解码器 , id 字段的值必须是 AV_CODEC_ID_H264 ;
/*** 标识比特流的语法和语义。* 原则大致是:* 具有相同ID的两个解码器可以解码相同的流。* 具有相同ID的两个编码器可以编码兼容的流。* 由于实现细节,可能会略有偏差。** 如果你向此列表添加一个编解码器ID,请遵循以下原则:* 1. 现有编解码器ID的值不发生变化(这会破坏ABI的兼容性),* 2. 新增的ID尽可能靠近相似的编解码器。** 在添加新的编解码器ID后,不要忘记在编解码器描述符列表中添加条目,* 并增加 libavcodec 的次版本号。*/
enum AVCodecID {AV_CODEC_ID_NONE, // 无编解码器ID/* 视频编解码器 */AV_CODEC_ID_H264, // H.264视频编解码器
}

源码地址 : https://github.com/FFmpeg/FFmpeg/blob/release/4.0/libavcodec/avcodec.h Line 245
二、FFmpeg 解码器相关 结构体 / 函数
1、AVFormatContext 结构体
音视频 解码 靠 " 解码器 " 进行 ;
与 解封装 类似 , 解封装器 工作 需要使用 AVFormatContext 格式上下文结构体 , 解封装相关信息都封装在该结构体中 ;
解码器 对音视频数据进行解码 , 也有一个 解码器上下文结构体 AVCodecContext ;
最新版本的 FFmpeg 使用 avcodec_alloc_context3 函数 , 分配 编解码器上下文 AVCodecContext 结构体 ;
- avcodec_alloc_context 和 avcodec_alloc_context2 是 早期版本 FFmpeg 中分配编解码器上下文结构体 的函数 , 现在已经弃用 , 如果在代码中遇到这两个函数需要注意 ;
AVCodecContext 用于存储 解码 或 编码 过程中使用的编解码器上下文信息 , 包含了大量的字段和配置信息 , 允许用户控制解码和编码的行为 ;
下面的代码中 列举了 一些重要的 AVCodecContext 结构体字段 ;
typedef struct AVCodecContext {const AVClass *av_class; // 指向AVClass的指针,用于支持FFmpeg的日志和调试功能int log_level_offset; // 日志级别偏移量enum AVMediaType codec_type; // 媒体类型,例如视频、音频、字幕等const struct AVCodec *codec; // 指向编码器或解码器的指针int codec_id; // 编解码器ID,指定要使用的编解码器类型(例如AV_CODEC_ID_H264)void *priv_data; // 指向私有数据的指针,用于存储编解码器特定的配置信息int bit_rate; // 目标码率(以比特/秒为单位)int width, height; // 视频宽度和高度int gop_size; // 视频的GOP(Group of Pictures)大小,设置I帧之间的间隔int max_b_frames; // 最大B帧数,B帧是一种双向预测的帧enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt; // 视频的像素格式(例如YUV420P)int sample_rate; // 音频采样率(以赫兹为单位)int channels; // 音频通道数enum AVSampleFormat sample_fmt; // 音频采样格式(例如AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLTP表示浮点格式)int64_t channel_layout; // 音频通道布局(例如立体声、5.1声道)int frame_size; // 每个音频帧的采样数int profile; // 编解码器的配置文件,例如H.264的Baseline、Main或High Profileint level; // 编解码器的级别,例如H.264中的Level 4.0int thread_count; // 线程数量,用于并行编码或解码int flags; // 编解码器的通用标志,用于设置不同的编码/解码选项int flags2; // 额外的标志选项AVRational time_base; // 基准时间,用于表示帧的时间戳AVRational framerate; // 视频帧率(以帧/秒表示)int64_t bit_rate_tolerance; // 比特率容忍度,用于VBR(可变比特率)编码int rc_buffer_size; // 码率控制缓冲区大小int rc_max_rate; // 最大比特率int rc_min_rate; // 最小比特率float qcompress; // 帧间压缩,用于调整比特率的波动float qblur; // 帧间模糊,用于平滑比特率变化int qmin; // 最小量化参数,用于控制编码质量int qmax; // 最大量化参数int64_t channel_layout; // 音频通道布局(例如立体声、5.1声道)// 省略许多其他字段
} AVCodecContext;
2、avcodec_find_decoder 函数 - 根据 ID 查找 解码器
avcodec_find_decoder 函数 用于 根据 解码器 ID 查找 指定解码器 , 函数原型如下 :
const AVCodec *avcodec_find_decoder(enum AVCodecID id);
- enum AVCodecID id 参数 : 指定要查找的 解码器的 ID , 这是一个枚举类型 , 用于标识各种支持的编解码器 , 如 : AV_CODEC_ID_H264 ;
- AVCodec * 返回值 :
- 如果 找到 对应的解码器 , 返回指向 AVCodec 结构体的指针 ;
- 如果 没有找到 对应的解码器 , 返回 NULL ;
代码示例 : 下面的代码是查找 H.264 解码器 的代码 ;
// 查找 H.264 解码器
const AVCodec *codec = avcodec_find_decoder(AV_CODEC_ID_H264);
if (!codec) {fprintf(stderr, "查找解码器失败\n");return -1;
}
3、avcodec_find_decoder_by_name 函数 - 根据 名称 查找 解码器
avcodec_find_decoder_by_name 函数 用于通过 解码器名称 查找 解码器 , 函数原型如下 :
const AVCodec *avcodec_find_decoder_by_name(const char *name);
- const char *name 参数 : 解码器名称 , H.264 解码器名称是 h264 ;
- AVCodec * 返回值 :
- 如果 找到 对应的解码器 , 返回指向 AVCodec 结构体的指针 ;
- 如果 没有找到 对应的解码器 , 返回 NULL ;
代码示例 : 下面的代码是根据 h264 名称查找解码器 ;
// 查找名为 "h264" 的解码器
const AVCodec *codec = avcodec_find_decoder_by_name("h264");
if (!codec) {fprintf(stderr, "查找解码器失败\n");return -1;
}
4、avcodec_alloc_context3 函数 - 初始化编解码上下文结构体
avcodec_alloc_context3 函数 用于分配并初始化一个 AVCodecContext 结构体 , 该结构体用于存储编解码器的上下文信息 , 函数原型如下 :
AVCodecContext *avcodec_alloc_context3(const AVCodec *codec);
- const AVCodec *codec 参数 : 指向 AVCodec 结构体的指针 , 该参数用于指定要使用的编解码器 , 如果为 NULL,会创建一个空的上下文,可以稍后再设置编码器 ;
- AVCodecContext * 类型返回值 : 如果初始化成功 , 则返回 编解码上下文结构体指针 , 如果初始化失败 , 返回 NULL ;
代码示例 : 下面的代码中 , 首先查找 h264 编解码器 , 然后为该编解码器分配上下文对象 ;
// 查找名为 "h264" 的解码器
const AVCodec *codec = avcodec_find_decoder_by_name("h264");
if (!codec) {fprintf(stderr, "查找解码器失败\n");return -1;
}// 分配编解码器上下文
AVCodecContext *codec_ctx = avcodec_alloc_context3(codec);
if (!codec_ctx) {fprintf(stderr, "分配编解码器上下文失败\n");return -1;
}
5、avcodec_parameters_to_context 函数 - 拷贝 编解码上下文结构体 数据
avcodec_parameters_to_context 函数 用于将 AVCodecParameters 中的参数拷贝到 AVCodecContext 中 , 函数原型如下 :
int avcodec_parameters_to_context(AVCodecContext *codec_ctx, const AVCodecParameters *par);
- AVCodecContext *codec_ctx 参数 : 指向 拷贝目的地 的 编解码器上下文 结构体 的 指针 , 这是 被拷贝的数据赋值的对象 ;
- const AVCodecParameters *par 参数 : 要 拷贝 的 编解码器参数 的 源结构体 , 数据从该结构体拷贝出来的 , 是数据源 ;
- int 返回值 :
- 拷贝成功 , 返回 0 ;
- 拷贝失败 , 返回负值 错误码 ;
代码示例 :
// 初始化 编解码器 上下文
AVCodecContext *codec_ctx = avcodec_alloc_context3(codec);
// 从 媒体流 中获取 编解码器参数 , 一般是被解码的音视频流
AVCodecParameters *par = stream->codecpar;// 将参数从 par 复制到 codec_ctx
if (avcodec_parameters_to_context(codec_ctx, par) < 0) {fprintf(stderr, "拷贝参数失败\n");return -1;
}
6、avcodec_open2 函数 - 打开编解码器
avcodec_open2 函数 用于打开指定的 编解码器 , 并与 AVCodecContext 关联 , 函数原型如下 :
int avcodec_open2(AVCodecContext *codec_ctx, const AVCodec *codec, AVDictionary **options);
- AVCodecContext *codec_ctx 参数 : 指向 AVCodecContext 结构体的指针 , 用于存储编解码器的上下文信息 ;
- const AVCodec *codec 参数 : 指向 AVCodec 结构体的指针 , 这是要打开的编解码器 ;
- AVDictionary **options 参数 : 指向 AVDictionary 的指针 , 这是用于传递编解码器的附加选项 , 一般都设置为 NULL ;
- int 返回值 :
- 打开成功 , 返回 0 ;
- 打开失败 , 返回负值 错误码 ;
代码示例 :
// 查找名为 "h264" 的解码器
const AVCodec *codec = avcodec_find_decoder_by_name("h264");
if (!codec) {fprintf(stderr, "查找解码器失败\n");return -1;
}// 分配编解码器上下文
AVCodecContext *codec_ctx = avcodec_alloc_context3(codec);
if (!codec_ctx) {fprintf(stderr, "分配编解码器上下文失败\n");return -1;
}// 打开解码器
if (avcodec_open2(codec_ctx, codec, NULL) < 0) {fprintf(stderr, "打开解码器失败\n");return -1;
}
7、avcodec_send_packet 函数 和 avcodec_receive_frame 函数 - 解码组合函数
avcodec_send_packet 函数 用于将 压缩数据包 发送到解码器 , 压缩数据包就是未解码的音视频帧 , 不能用于播放 , 函数原型如下 :
int avcodec_send_packet(AVCodecContext *codec_ctx, const AVPacket *pkt);
- AVCodecContext *codec_ctx 参数 : 指向 编解码器 上下文 结构体的指针 ;
- const AVPacket *pkt 参数 : 指向 AVPacket 结构体的指针 , 其中包含编码数据的包 , 如果设置为 NULL , 表示解码器接收的输入数据已经结束 ;
- int 类型 返回值 :
- 发送成功 返回 0 ;
- 发送失败 返回 负值错误码 ;
avcodec_receive_frame 函数 用于从 解码器 获取 解码后的 音视频帧 , 该 音视频帧 可直接用于播放 , 函数原型如下 :
int avcodec_receive_frame(AVCodecContext *codec_ctx, AVFrame *frame);
- AVCodecContext *codec_ctx 参数 : 指向 编解码器 上下文 结构体的指针 ;
- AVFrame *frame 参数 : 接收到的 解码后的 音视频帧 数据 ;
- int 类型 返回值 :
- 接收成功 返回 0 ;
- 接收失败 返回 负值错误码 ;
代码示例 :
// 初始化解码器上下文 codec_ctx,并确保其已成功打开AVPacket pkt; // 定义一个 AVPacket 结构,用于存储压缩数据包
AVFrame *frame = av_frame_alloc(); // 分配一个 AVFrame 结构,用于存储解码后的帧
int ret; // 定义返回值变量,用于存储函数返回的状态// 向解码器发送压缩包
ret = avcodec_send_packet(codec_ctx, &pkt); // 将压缩数据包发送给解码器
if (ret < 0) { // 如果发送数据包失败fprintf(stderr, "Error sending packet to decoder\n"); // 输出错误信息
}// 从解码器接收解码后的帧
while (ret >= 0) {ret = avcodec_receive_frame(codec_ctx, frame); // 从解码器接收解码后的帧if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN) || ret == AVERROR_EOF) { // 如果没有更多帧可以接收或已到文件末尾break; // 退出循环} else if (ret < 0) { // 如果接收解码帧过程中出错fprintf(stderr, "Error during decoding\n"); // 输出错误信息break; // 退出循环}// 使用解码后的 frame(例如渲染或进行其他处理)av_frame_unref(frame); // 清除帧数据,准备接收下一帧
}av_frame_free(&frame); // 释放 frame 结构,避免内存泄漏
8、avcodec_free_context 函数 和 avcodec_close 函数 - 释放编解码器上下文结构体
avcodec_free_context 函数 用于释放 AVCodecContext 结构体并清除其中的所有资源 , 函数原型如下 :
void avcodec_free_context(AVCodecContext **codec_ctx);
- AVCodecContext **codec_ctx 参数 : 指向 AVCodecContext 指针的 指针 , 这是要释放的编解码器上下文 , 该函数会将 *codec_ctx 置为 NULL ;
avcodec_free_context 函数 会自动调用 avcodec_close 函数 ;
avcodec_close 函数 用于关闭一个打开的 AVCodecContext 结构体 , 释放与其关联的编解码器资源 , 函数原型如下 :
int avcodec_close(AVCodecContext *codec_ctx);
- AVCodecContext **codec_ctx 参数 : 指向 AVCodecContext 指针的 指针 , 这是要释放的编解码器上下文 , 该函数会将 *codec_ctx 置为 NULL ;
