历久弥新的c-Met:靶向疗法研究进展
前 言
c-Met属于人体内原癌基因编码的蛋白质,与配体HGF结合,激活多条重要的信号通路。C-Met/HGF参与广泛的细胞过程,如细胞增殖、迁移和转移,以及组织修复等,同样也会促进肿瘤的生成和转移。目前,FDA批准的靶向c-Met的药物超过6种,还有40多种处于临床试验阶段,其中双抗、ADC及CAR-T等疗法临床前效果较好。
01 c-Met:结构及功能
c-Met,细胞间质-上皮转化因子,属于酪氨酸激酶受体家族,在多种人类肿瘤中过表达,其配体是肝细胞生长因子HGF。c-Met最初在体内翻译成一条单链前体蛋白,随后经过翻译后修饰而成为由二硫键连接的成熟受体。c-Met/HGF信号转导在胚胎发育、组织修复和伤口愈合中起到至关重要的作用。c-Met蛋白通常在上皮细胞中表达,是一种与生长、运动和浸润相关的多功能调节因子。
c-Met的细胞外部分包括三个结构域,一个N端SEMA结构域、一个富半胱氨酸结构域和四个IPT结构域。细胞内部分包括酪氨酸激酶催化结构域、膜旁结构域和羧基末端序列。HGF包含两个受体结合位点:一个对c-Met的IPT3和IPT4结构域具有高亲和力的结合位点,一个对SEMA结构域具有低亲和力的结合位点。
二聚化是激活酪氨酸激酶受体的潜在调节机制。c-Met与HGF结合后,发生二聚化,激活环内的Tyr残基Y1234和Y1235发生反式自磷酸化,为下游信号效应分子的募集提供结合位点。具有酶活性的结合蛋白包括PI3K、PLC-γ1、SRC、STAT3、GRB2、GAB1等,进而激活PI3K/AKT、Ras/MAPK、JAK/STAT、SRC、Wnt/β-catenin等多个信号通路。
在正常生理条件下,HGF/c-Met在胚胎发生、组织再生、伤口愈合以及神经和肌肉的形成中起作用,由肿瘤抑制因子p53介导。越来越多的证据表明,HGF/c-Met调控异常和c-Met基因突变、扩增和过表达导致了大量人类疾病,尤其是癌症。
02 c-Met:历久弥新的靶点
在肝癌、肺癌、结肠癌、乳腺癌、胰腺癌、卵巢癌、前列腺癌和胃癌以及其他癌症等多种恶性肿瘤中观察到c-Met失调。c-Met的过表达或突变导致信号转导异常活跃,促进肿瘤生长、血管生成和癌症转移。c-Met/HGF轴在肿瘤免疫中发挥着重要作用,因此是一个引人关注的治疗靶点。
目前,FDA批准的靶向c-Met药物超过6种。然而,值得注意的是,直接抑制HGF/c-Met轴(大多数获批药物的主要作用机制)可能导致获得性耐药的发生。据统计,目前有超过40种c-Met靶向药物正处于临床试验阶段。其中,双特异性抗体(bsAb)、抗体药物偶联物(ADC)以及CAR-T细胞和小分子等方法在晚期临床试验阶段和临床前研究中显示出可喜的结果。
| 处于临床前和临床阶段的c-Met靶向疗法 (截止23年5月) | |||
| 名称 | 类型 | 研究阶段 | 适应症 |
| Amivantamab | Bispecific Antibody | Phase 3 | SCLC |
| Emibetuzumab | Monoclonal Antibody | Phase 2 | SCLC |
| TR1801-ADC | Antibody-drug conjugate | Phase 1 | Solid tumors |
| Telisotuzumab vedotin | Monoclonal Antibody | Phase 2 | SCLC |
| Anti-C-met CAR-T cells | CAR-T cells | Phase 1/2 | Colorectal cancer |
| scFv CAR | CAR-T cells | Phase 1 | Melanoma |
| SHR-A1403 | Antibody-drug conjugate | Preclinical | Solid tumors |
| NPS-1034 | Small molecule | Preclinical | Solid tumors |
03 c-Met:研究应用
义翘神州的产品经常发表于高分期刊,助力细胞治疗、抗体药开发、免疫治疗等领域的研究。
Park等人使用义翘神州的重组蛋白c-Met研究了IRCR201与人和小鼠c-Met胞外域的结合模式,并证实此抗体通过抑制c-Met信号通路进而抑制肿瘤生长。
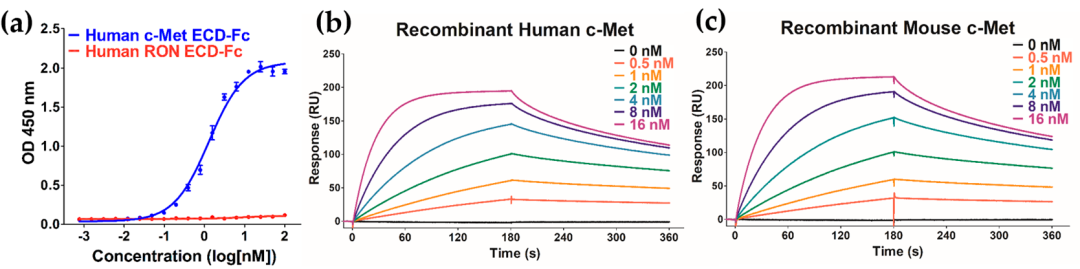
Binding properties of IRCR201. (a) Binding patterns of IRCR201 to the human c-Met extracellular domain (ECD) fragment crystallizable region (Fc) and the human RON (recepteur d'origine nantais) ECD-Fc were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). IRCR201 binds to the human c-Met ECD-Fc with specificity and selectivity. (b and c) Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensorgrams binding with varying concentrations of IRCR201 to human c-Met, mouse c-Met. Human c-Met ECD-Fc (Sino Biological, 10692-H03H) and mouse c-Met ECD-Fc (Sino Biological, 50622-M02H)
Chen等人利用c-Met作为对照,评估经PRO-6E处理的内源性c-Met的降解情况,认为PRO-6E可用于c-Met依赖性胃癌的治疗。
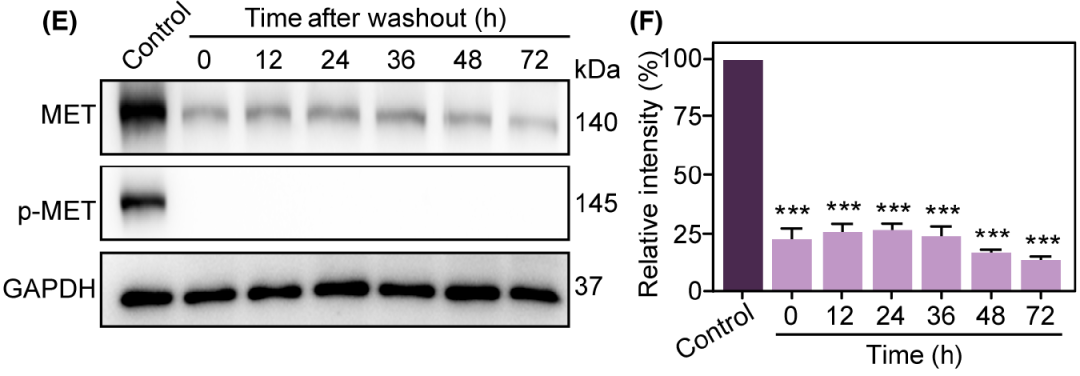
PRO-6 E was a MET degrader. (E) MET and p-MET expression. Following PRO-6 E (1 μM, 48 h) treatment, the compound was removed, and the incubation continued for the specified amount of time. MET protein (Sino Biological, 10692-H08H)
Makowski等人采用荧光激活细胞分选技术测量c-Met与酵母表面展示Bococizumab库的结合亲和力,扩展对新型抗体的探索。
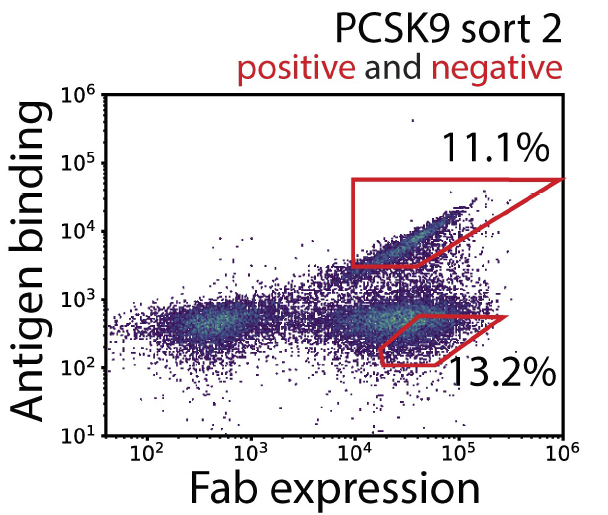
Design and sorting of a bococizumab Fab library. Bococizumab library displayed on the surface of yeast was enriched for high and low levels of antigen binding (c-Met/PCSK9, 2 sorts) using fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Biotinylated c-Met/PCSK9 (Sino Biological, 10692-H27H-B) was used in binding affinity assay.
Jiang等人使用APC标记c-Met抗体检测肿瘤细胞表面c-Met的表达,用于验证CAR-T细胞的抗肿瘤效果。

In Flow cytometric analysis, the expression of c-Met on tumor cells was examined by incubating with APC-conjugated anti-c-Met antibody (Sino Biological, 10692-R243-A).
✦义翘神州c-Met特色产品
义翘神州提供高质量的c-Met产品,这些产品经过严格的质量控制,获得广大客户认可,成功助力客户发表多篇顶级期刊。
人 c-Met 蛋白(HPLC验证,4篇文献)(货号:10692-H08H)
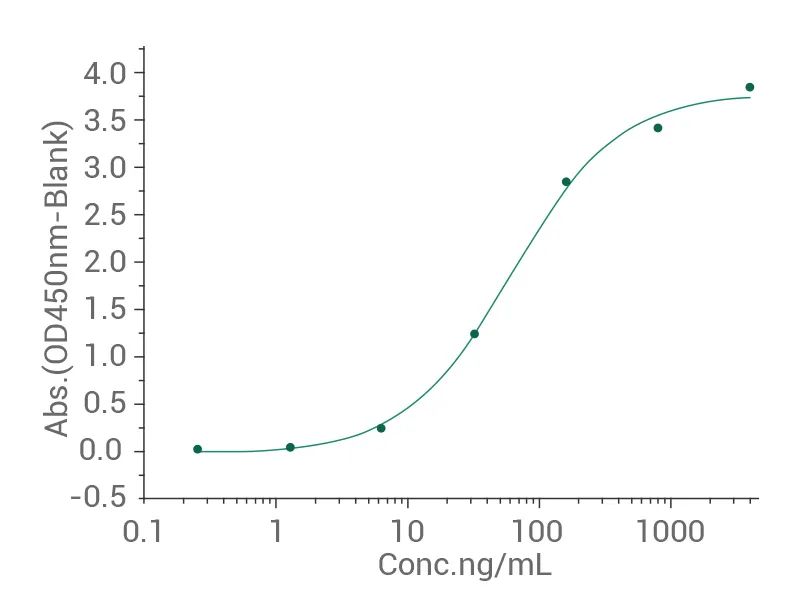
Immobilized Cynomolgus HGF can bind to Human c-Met
小鼠 c-Met 蛋白(11篇文献)(货号:50622-M02H)
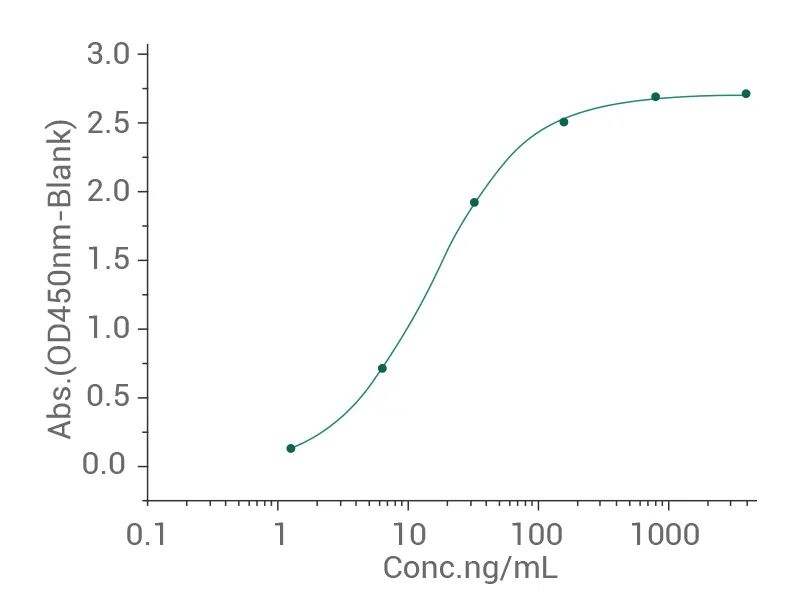
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized human HGF can bind mouse c-Met.
| 义翘神州c-Met重组蛋白(部分) | |||
| 货号 | 种属 | 标签 | 纯度及活性 |
| 10692-H27H-B | Human | His-Avi | >90%, Active |
| 50622-M08H | Mouse | His | >90%, Active |
| 80004-R08H | Rat | His | >90%, Active |
| 90304-C08H | Cynomolgus/Rhesus | His | >90%, Active |
| 70008-D08H | Canine | His | >95%, Active |
【参考文献】
1. Y. Zhang et al. Function of the c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase in carcinogenesis and associated therapeutic opportunities. Molecular Cancer 2018.
2. Y. Zhou et al. Therapeutic target database update 2022: facilitating drug discovery with enriched comparative data of targeted agents. Nucleic Acids Research 2021.
3. X. Huang et al. Targeting the HGF/MET Axis in Cancer Therapy: Challenges in Resistance and Opportunities for Improvement. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 2020.
4. E. K. Makowski et al. Reduction of therapeutic antibody self-association using yeast-display selections and machine learning. mAbs 2022.
5. E. K. Makowski et al. Co-optimization of therapeutic antibody affinity and specificity using machine learning models that generalize to novel mutational space. Nature Communications 2022.
6. W. Jiang et al. Bispecific c-Met/PD-L1 CAR-T Cells Have Enhanced Therapeutic Effects on Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Frontiers in Oncology 2021.
7. H. K. Park et al. Tumor Inhibitory Effect of IRCR201, a Novel Cross-Reactive c-Met Antibody Targeting the PSI Domain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2017.
8. J. J. Chen et al. Crizotinib-based proteolysis targeting chimera suppresses gastric cancer by promoting MET degradation. Cancer Science, Jan. 2023.
