二叉树方面的题
题目:236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个节点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个节点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
示例 1:
输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1 输出:3 解释:节点5和节点1的最近公共祖先是节点3 。
示例 2:
输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4 输出:5 解释:节点5和节点4的最近公共祖先是节点5 。因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
示例 3:
输入:root = [1,2], p = 1, q = 2 输出:1
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[2, 105]内。 -109 <= Node.val <= 109- 所有
Node.val互不相同。 p != qp和q均存在于给定的二叉树中。
思路:1.判空,空树无祖先;
2.判断p,q是否等于头结点
3.递归左右子树
分三种情况:
1.左右都不为空,返回根节点;
2.左不为空,返回左树;
3.右不为空,返回右树。
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }* }*/
class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {//判空if(root==null){return null;}//判断p,q是否在根节点if(root==q||root==p){return root;}//递归左右子树TreeNode leftTree=lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);TreeNode rightTree=lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);if(leftTree!=null&&rightTree!=null){return root;}else if(leftTree!=null){return leftTree;}else{return rightTree;}}
}方法二:
以求链表的相交节点的方法写:
先判空,实例化两个栈P,Q,
找到p,q距离根节点的路径,写一个方法,1.先判空,根节点和node节点都要找2.先入栈顶元素,判断栈顶元素是否等于要找的节点,如果不是,则去递归左右子树去找,都没有则弹出栈顶元素。
求栈的大小,先走差值步,然后两个同时走,相等则返回相等的节点。
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }* }*/
class Solution {private boolean getPath(TreeNode root, TreeNode node, Stack<TreeNode> stack){if(root==null||node==null){return false;}//先入一个根节点stack.push(root);if(root==node){return true;}//递归左右子树,找目标节点boolean flg=getPath(root.left,node,stack);if(flg==true){return true;}boolean flg2=getPath(root.right,node,stack);if(flg2==true){return true;}stack.pop();return false;}//用栈求交点public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (root == null) {return null;}//实例化两个栈,Stack<TreeNode> stackP = new Stack<>();Stack<TreeNode> stackQ = new Stack<>();getPath(root, p, stackP);getPath(root, q, stackQ);//对栈进行操作,求p,q的大小int sizeP = stackP.size();int sizeQ = stackQ.size();//先走差值步if (sizeP > sizeQ) {int size = sizeP - sizeQ;while (size != 0) {stackP.pop();size--;}} else {int size = sizeQ - sizeP;while (size != 0) {stackQ.pop();size--;}}//两个同时走,如果相等,则随便返回一个相等的值,如果不相等,则出栈继续找while (!stackP.isEmpty() && !stackQ.isEmpty()) {if (stackP.peek().equals(stackQ.peek())) {return stackP.peek();}stackP.pop();stackQ.pop();}//都没有则返回空return null;}
}题目:105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定两个整数数组 preorder 和 inorder ,其中 preorder 是二叉树的先序遍历, inorder 是同一棵树的中序遍历,请构造二叉树并返回其根节点。
示例 1:
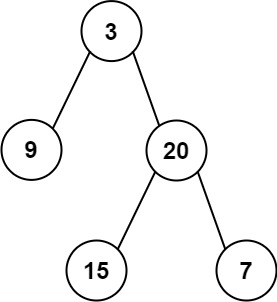
输入: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7] 输出: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
示例 2:
输入: preorder = [-1], inorder = [-1] 输出: [-1]
提示:
1 <= preorder.length <= 3000inorder.length == preorder.length-3000 <= preorder[i], inorder[i] <= 3000preorder和inorder均 无重复 元素inorder均出现在preorderpreorder保证 为二叉树的前序遍历序列inorder保证 为二叉树的中序遍历序列
思路:
1.创建根节点,
2.在中序遍历中找根节点所对应的下标
3.递归创建左右子树
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {public int priIndex;//成员变量,局部变量容易造成死循环public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {return buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);}private TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] preorder,int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend) {//没有左树或没有右数了(inbegin>inend)if(inbegin>inend){return null;}//创建根节点TreeNode root =new TreeNode(preorder[priIndex]);//找到前序遍历在中序遍历中对应的根节点的下标int rootIndex=findIndex(inorder,inbegin,inend,preorder[priIndex]);if(rootIndex==-1){return null;}priIndex++;//创建左子树和右子树root.left=buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,inbegin,rootIndex-1);root.right=buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,rootIndex+1,inend);return root;}//找中序遍历中根节点所在的位置private int findIndex(int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend,int key){//循环遍历,相等则返回下标for (int i=inbegin;i<=inend;i++){if(inorder[i]==key){return i;}}return -1;}
}题目:106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定两个整数数组 inorder 和 postorder ,其中 inorder 是二叉树的中序遍历, postorder 是同一棵树的后序遍历,请你构造并返回这颗 二叉树 。
示例 1:

输入:inorder = [9,3,15,20,7], postorder = [9,15,7,20,3] 输出:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
示例 2:
输入:inorder = [-1], postorder = [-1] 输出:[-1]
提示:
1 <= inorder.length <= 3000postorder.length == inorder.length-3000 <= inorder[i], postorder[i] <= 3000inorder和postorder都由 不同 的值组成postorder中每一个值都在inorder中inorder保证是树的中序遍历postorder保证是树的后序遍历
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {public int postIndex;//成员变量,局部变量容易造成死循环public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {postIndex=postorder.length-1;return buildTreeChild(postorder,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);}private TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] postorder,int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend) {//没有左树或没有右数了(inbegin>inend)if(inbegin>inend){return null;}//创建根节点TreeNode root =new TreeNode(postorder[postIndex]);//找到后序遍历在中序遍历中对应的根节点的下标int rootIndex=findIndex(inorder,inbegin,inend,postorder[postIndex]);if(rootIndex==-1){return null;}postIndex--;//创建左子树和右子树root.right=buildTreeChild(postorder,inorder,rootIndex+1,inend);root.left=buildTreeChild(postorder,inorder,inbegin,rootIndex-1);return root;}//找中序遍历中根节点所在的位置private int findIndex(int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend,int key){//循环遍历,相等则返回下标for (int i=inbegin;i<=inend;i++){if(inorder[i]==key){return i;}}return -1;}}